Amnioquick® Test
Amnioquick® is a simple and rapid in vitro test for detection of premature rupture of foetal membranes (PROM) in pregnant woman. Preterm prelabour rupture of membranes (P-PROM) is the rupture of membranes prior to the onset of labour, in a patient who is at less than 37 weeks of gestation.
Most women go into spontaneous labour within 24 hours of rupturing their membranes but 6% of women will not be in spontaneous labour within 96 hours. However, the earlier the rupture occurs in gestation, the less likely that the onset of labour will be within a specified time period.
Amnioquick® is a simple, rapid and sensitive test for detection of Insulin Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 (IGFBP-1) from vaginal swab samples. Based on monoclonal antibody technology Amnioquick® can detect IGFBP-1 at concentrations of 5 ng/mL test with no interference from other proteins. The test is sensitive enough to detect IGFBP-1 in a few microliters of amniotic fluid.
Important notes
In vitro diagnostic use only.
To be used by trained healthcare professionals.

Quick and Reliable
- Easy to perform testing
- Results in 10 minutes
- Easy storage and handling
- The Amnioquick test has a high sensitivity and specificity.
Clinical Significance
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM) can occur in 5- 10% of pregnancy cases, which could result in preterm delivery and foetal infection. Accurate diagnosis is essential for proper management of PROM. This cannot always be detected in conventional clinical examination, so a immunochromatographic test is often needed as confirmation. Biological tests can be based on detection of vaginal alkalisation which may not always be conclusive or detection of molecules which are physiologically present in high concentrations in the amniotic fluid.
Epidemiology (from: https://patient.info/doctor/preterm-prelabour-rupture-of-membranes)
- PROM occurs in 6-19% of term pregnancies.[1]
- P-PROM occurs in 2% of all pregnancies.[2]
- P-PROM is associated with 40% of preterm deliveries and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Risk factors
Risk factors for P-PROM are:
- Smoking: heavy cigarette smoking increases the risk of P-PROM. The increased risk is greatest at gestational ages lower than 28 weeks.[3]
- Previous preterm delivery.
- Vaginal bleeding (at any time during the pregnancy).
- There is an association between lower genital tract infection and P-PROM.
- Around a third of women with P-PROM have positive amniotic fluid cultures.[2]
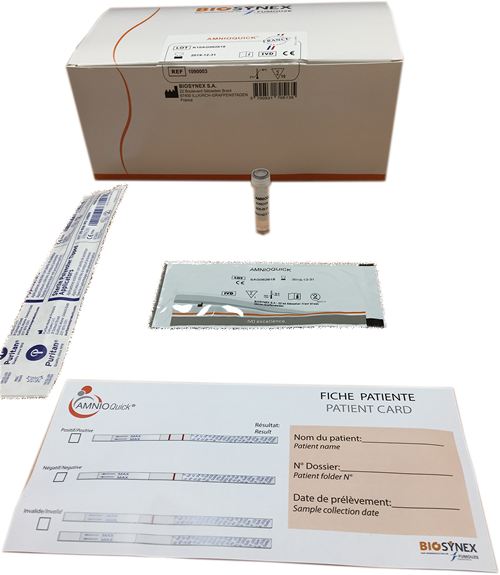
Test Kit Includes
- Test Dip Sticks (10 tests)
- Sterile dacron vaginal swab
- Unit dose vial of diluent
- Rack tube
- 1 package insert
Sample Type
- Vaginal secretion
Type of measurement
- Qualitative
Testing Time
- 10 minutes
Storage
- 2 – 30 °C Until expiry date
Operating Temperature
- Room Temperature (15 – 30 °C)
User Guide
Guidance
- Induction of labour; NICE Clinical Guideline (July 2008 - currently under review)
- Preterm Prelabour Rupture of Membranes (November 2006 - minor amendment October 2010); Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- England MC, Benjamin A, Abenhaim HA; Increased Risk of Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes at Early Gestational Ages among Maternal Cigarette Smokers. Am J Perinatol. 2013 Jan 17
- Preterm labour and birth; NICE Guidelines (November 2015)
- Intrapartum care: care of healthy women and their babies during childbirth; NICE Clinical Guideline (Dec 2014)